What It’s Like to Struggle Daily With Agoraphobia
Published on November 8th, 2018
Updated on January 2nd, 2024
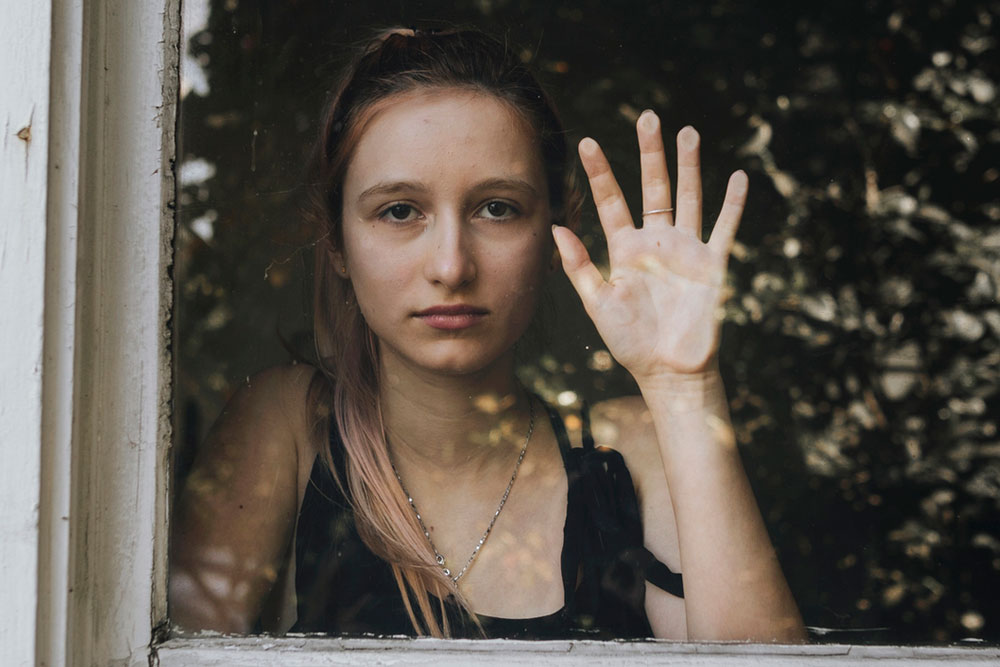

People who suffer from agoraphobia have an intense fear of certain places and situations. People who suffer from agoraphobia fear being in a situation that may be difficult to escape from. This fear is paired with a fear of having a panic attack or of being embarrassed in some way.
A person with agoraphobia will have intense anxiety about entering feared environments. They will avoid these situations as much as possible. In severe cases, affected people will struggle to leave their home.
Fears That Stem From Agoraphobia
The most popular impression of agoraphobia is a fear of leaving the home. While many affected people may fear leaving their homes, others with agoraphobia do not suffer from this fear.
Sponsored by

Choose a therapist to work with and start healing with 20% off from BetterHelp.
Click HereA person who suffers from agoraphobia fear situations in which they feel out of control. Their fears will stem from either having a panic attack in public or having an embarrassing moment that they cannot escape from.
Situations that may cause fear or panic for people with agoraphobia include:
- Using public transportation
- Being in open spaces, like parks, grocery, warehouse stores, or parking lots
- Being in enclosed public spaces, like theaters, malls, or party venues
- Being in a crowd of people
- Standing and waiting in line
- Being alone while out of the house
A person with agoraphobia will try to avoid their feared situation. They will fear being in a space that they perceive as inescapable.
Symptoms of Agoraphobia
Any of the triggering situations cause uncomfortable symptoms for a person with agoraphobia. Such symptoms include:
- Panic attacks
- Intense anxiety, even at the thought of entering the feared situation
- Avoidance of the feared situation
- A need to have a friend or family member present to feel okay in the feared situation
- A perceived danger of a situation that is excessive, imagined, or exaggerated
Fear and avoidance symptoms may for at least 6 months. They will significantly impact a person’s ability to function. This may impair the following:
- Career and occupational responsibilities and goals
- Education and academic performance
- Family and personal relationships
- Financial or job security
A person’s comfort in social situations may also be affected. However, this discomfort is not due to social anxiety. Discomfort stemming from social anxiety is considered a different mental health disorder.
Risk Factors for Agoraphobia
Agoraphobia is often related to a case of panic disorder. It may also co-occur with other mental health disorders. People who also suffer from another mental health disorder tend to have more intense symptoms of agoraphobia. Such mental health disorders that may affect a case of agoraphobia include:
- Generalized anxiety disorder
- Depression
- Substance use disorders
- Panic disorder
- Somatic symptom disorders
A person’s personal history will affect the risk of agoraphobia. There are risk factors that can increase the risk of a person suffering from the condition. Such risk factors include:
A Family History of Agoraphobia. Agoraphobia can run in families. This can be due to genetics or modeling from other family members.
Childhood Upbringing. How a child is raised can affect the risk of agoraphobia. A child who grew up with overprotective parents may be at risk of developing the condition. Experiencing the loss of a parent may also increase risk. The loss may be due to death, abandonment, divorce, etc.
Experiencing A Stressful Event Outside Of The Home. Experiencing an event that is unexpected and stressful can increase the risk of agoraphobia.
Example: A person who is attacked, robbed, or humiliated by a stranger may be at risk of developing agoraphobia.
Personality Traits. Certain personality traits are associated with agoraphobia. Neuroticism and sensitivity to anxiety can increase the risk of agoraphobia. A resistance to engaging in overwhelming or unfamiliar environments can increase risk as well.

Treatment Options for Agoraphobia
Agoraphobia is considered a progressive disorder. This means that it is triggered by something and can become worse if no intervention is taken. Treatment is especially needed if symptoms and fears last for 6 months or longer.
Early intervention is key for recovery from agoraphobia. Therapy for agoraphobia consists of talk therapy that addresses the affected person’s fears. Medication may be recommended for some cases of the condition.
Effective treatment options for agoraphobia include:
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) teaches people with agoraphobia how to understand the difference between anxious thoughts and real-life high-risk situations.
This process helps the affected person learn how to identify real vs. imagined danger in different settings. It also teaches methods of managing anxiety.
Exposure Therapy is a process of gradually exposing the affected person to feared situations. This gradual and repeated exposure is used to lessen the intensity of the fear response.
The process begins at mild exposure to feared situations and progresses to more frequent and intense exposure. This approach is taken at the client’s pace, which helps to boost confidence and authority in the process.
Sponsored by

Find an affordable therapist online with 20% off from BetterHelp.
Click Here






Leave A Reply