What It’s Like To Have Borderline Personality Disorder
Published on June 6th, 2018
Updated on January 4th, 2024
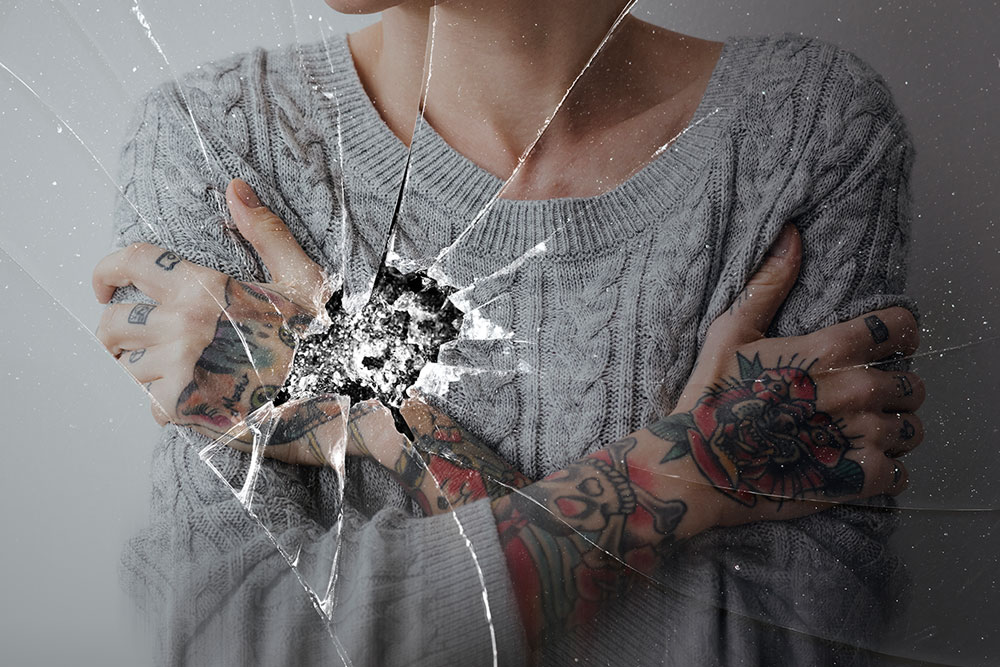

Borderline personality disorder (BPD) causes a person to feel insecure in relationships. A person with BPD struggles with self-image and mood swings. They may act impulsively and struggle to create secure attachments with others.
People with BPD struggle to create and maintain healthy relationships. They engage in testing behaviors that build insecurity and distrust for friends and loved ones. The behavior that a person with BPD may show can be described as push-and-pull behavior. This is because affected people push loved ones away but then become angry and possessive when they feel distanced from them.
People with BPD are terrified of being abandoned. This fear of abandonment can cause them to feel like they must flee a relationship before they are abandoned. This causes unstable relationships and deeply-rooted issues with self-esteem and trust.
Sponsored by

Choose a therapist to work with and start healing with 20% off from BetterHelp.
Click HereIf left untreated, BPD can have long-lasting consequences on an affected person. It is important to seek professional help if you suspect that you are suffering from BPD.
Symptoms and Warning Signs of Borderline Personality Disorder
Symptoms of BPD can look similar to other disorders. It is often mistaken for depression or bipolar disorder because of the similarities in symptoms.
A person will show signs of BPD through their mood, thoughts, and behaviors. Their symptoms will affect their ability to create secure relationships with others. They will also impact their quality of life if left untreated.
Symptoms and warning signs of BPD include:
- A pattern of unstable relationships
- Extreme mood swings
- Co-occurring mood disorders
- Anxiety
- Bipolar disorder
- Depression
- Bipolar disorder
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Intense fear of abandonment
- Desperate efforts to avoid abandonment
- Feelings of emptiness
- Alternating patterns of romanticizing and devaluing relationships
- Paranoia
- Suicidal thoughts or threats
- Self-harm
- Impulsive and sometimes dangerous behavior
- Irresponsible or Impulsive spending
- Promiscuous or irresponsible sexual behavior
- Rash decision making
- Substance use
- Low self-esteem and unstable self-image
- Difficulty managing anger
- Being combative with loved ones
A person with BPD will exhibit a habit of “pushing and pulling” in relationships. They will go from desperately needing to be close to a partner to acting hostile or unapproachable toward them.
In severe cases, the person with BPD may show psychotic or dissociative symptoms. Psychotic symptoms are signs of a person falling out of touch with reality. Dissociative symptoms cause a person to feel disconnected from their physical body. This can feel like you are an observer of what is going on around you.

Causes and Risk Factors of Borderline Personality Disorder
The cause of a case of BPD may vary. It can be caused as a result of different circumstances. Typically, a case of BPD involves fear or experience with insecurity in relationships. They may have experienced abandonment or learned that love and acceptance from others are conditional.
The following life experiences can cause people to develop BPD:
Genetic Factors. Family history is an important consideration for the risk of developing BPD. The condition can run in families, and a child is at higher risk if they have a parent or sibling who also suffered from BPD.
Environmental Factors. The circumstances in which a person is brought up affect the risk of BPD. A child who lived in an unstable or chaotic home may be at increased risk of BPD. A child may also be at risk if they were exposed to hostile fighting or conflict between parents or family members.
Social Factors. Children who were victims of criticism or were made to feel unloved or unvalued during childhood may develop BPD. This may be due to bullying in social groups or criticism and feeling conditional love and acceptance at home.
A History Of Trauma. People who have a history of trauma or abuse are at increased risk of developing BPD. Trauma and abuse may have occurred during childhood or adulthood. Adults who endured relationship abuse may be at increased risk of developing the condition.
A History Of Neglect. Growing up in a neglectful environment is also a risk factor. There are many kinds of neglect, like physical, mental, and emotional neglect. In these cases, children learn unhealthy methods to cope with neglect.
Although these factors may increase a person’s risk, it does not mean that they will develop BPD. Likewise, there may be people without these risk factors who develop BPD.
Treatment for Borderline Personality Disorder
Treatment for BPD can be challenging. It requires a lot of personal growth that comes from confronting unhealthy beliefs. These beliefs revolve around the affected person’s self-worth and how they relate to others. As a person with BPD grows in treatment, they learn new things about themselves that challenge their belief systems. This process can be uncomfortable and difficult to trust without practice.
While it may be difficult, it is possible to treat BPD. Dialectical behavioral therapy (DBT) was developed specifically to help people with BPD. This form of therapy helps people with BPD learn how to cope with emotional stress. It also challenges problem behaviors and distorted thinking, which helps with creating a healthier self-image. DBT teaches coping strategies like distress tolerance and emotional regulation, which helps when learning how to build and maintain healthy relationships.
Sponsored by

Find an affordable therapist online with 20% off from BetterHelp.
Click Here






Leave A Reply