Treatment Options For Agoraphobia
Published on September 17th, 2019
Updated on January 2nd, 2024
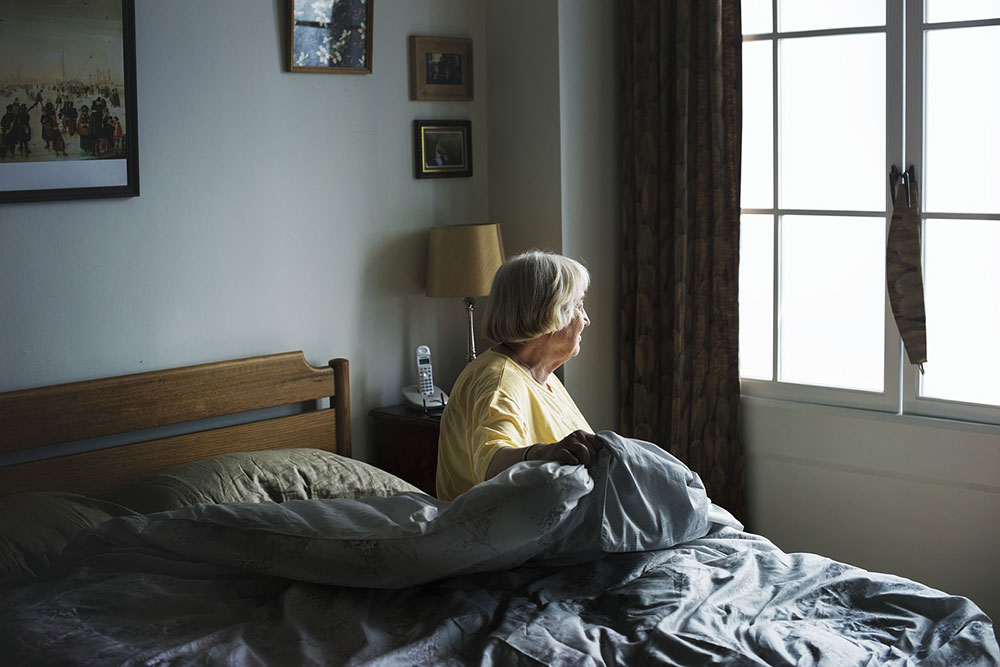

Agoraphobia is a condition that causes a fear of situations that are perceived to be inescapable. People who suffer from agoraphobia struggle with excessive fears and anxiety for triggering situations. This fear causes them to avoid situations that they feel compromise their wellness.
People with agoraphobia are fearful of different kinds of environments and situations. Some may even fear leaving their homes. Some affected people can be in the feared environment for short amounts of time despite the fear. When in the feared environment, they suffer from anxiety and may need a companion to feel safe.
Common Situations That Trigger People With Agoraphobia
Several different situations can trigger anxiety for a person with agoraphobia. These situations often involve a scenario where there is a perceived threat. The sense of risk for being in such a situation is imagined or excessive.
Sponsored by

Choose a therapist to work with and start healing with 20% off from BetterHelp.
Click HereMost situations that cause a person to feel fear and anxiety are relatively harmless. A person with anxiety may fear something bad happening without a means to escape. This fear includes having a panic attack or anxiety reaction. There also may be a fear of being humiliated in some way without a means to escape public scrutiny.
Common places and situations that can trigger agoraphobia include:
- Public transportation (buses, trains, planes, taxis, etc.)
- Wide-open spaces
- Public places
- Enclosed spaces
- Attending appointments
- Being in spaces where there are only one or few exits
- Crowded spaces
- Unfamiliar situations or settings
Consequences of Agoraphobia
Agoraphobia causes a person to live their life in fear. They can be fearful of most places, which takes a toll on their quality of life. As a result, many areas of an affected person’s life are significantly affected.
Consequences of agoraphobia include:
- Challenges with running errands or keeping up with responsibilities
- Trouble with socializing or making friends
- Struggling to maintain friendships and relationships with family
- Depression due to a lack of social interaction with others
- Difficulty of taking care of physical, medical, and mental health needs
- Challenges with pursuing education and career goals
- Difficulty with enjoying social activities with others
- Difficulty with engaging in enjoyable activities outside of the home
Agoraphobia can co-occur with other mental health conditions. Conditions that can occur with agoraphobia include:
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Panic Disorder
- Somatic Symptom Disorders
Treatment Options For Agoraphobia
Agoraphobia treatment is challenging. It requires a person to confront their fears and step out of their comfort zone. This helps them to learn how to cope with their anxiety, fears, and avoidance of unfamiliar places.
Commitment to therapy for agoraphobia can result in recovery. It takes time and commitment to change. It also requires patience and forgiveness for one’s anxieties and challenges.
Therapy for agoraphobia teaches a person how to manage symptoms with coping skills. In therapy, a person learns how to manage their fears to reduce anxiety.
The following forms of therapy are often used in the treatment of agoraphobia:
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
CBT is a form of therapy that is commonly used in the treatment of agoraphobia. CBT teaches an affected person how to face their fears.
In CBT, a person learns how to separate their anxious thoughts from the feared situation. They learn that their anxious thoughts are what cause their fear and panic. They also learn how avoiding feared situations reinforces the fear within themselves.
CBT targets a person’s immediate thoughts in reaction to a trigger. It helps the affected person learn how to confront their fears by challenging anxious thoughts. The more anxious thoughts are challenged, the less powerful they become. This, in turn, makes the fear response less intense.
Exposure Therapy
Exposure therapy is a form of therapy that helps an affected person confront their fears. Exposure therapy intends to lessen the fear response to triggers.
The goal of exposure therapy is to desensitize the fear response. This reduces feelings of anxiety and distress when facing the trigger in real life.
There are different types of exposure therapy, including:
- In Vivo Exposure. Confronting your fear in real life.
- Imaginal Exposure. Being guided through a process of confronting your fear through your imagination.
- Virtual Reality Exposure. Using virtual reality programs to confront your fear through simulation.
- Interoceptive Exposure. Facing fears by recreating symptomatic feelings in a safe space.
Example: Taking fast, deep breaths to emulate hyperventilation.
People participating in exposure therapy may also use a hierarchy of fears. With this approach, an affected person organizes their feared situations from most tolerable to least tolerable. This hierarchy is used as a guide to building resistance to triggers.
Psychiatric Medication
Psychiatric medication may also be recommended in some cases of agoraphobia. In more severe cases, medication can help ease symptoms while working on coping skills.
It is important to note that treatment is most effective with therapy. Medication alone is not enough to treat agoraphobia. While medication can ease symptoms, it is important to also learn coping skills for managing triggers.
If psychiatric medication is recommended, the affected person will be asked to meet with either:
- psychiatrist, or
- a psychiatric nurse practitioner.
The prescribing professional may coordinate care with the affected person’s therapist.
Sponsored by

Find an affordable therapist online with 20% off from BetterHelp.
Click Here






Leave A Reply