Humanistic Approach
Published on February 4th, 2021
Updated on January 2nd, 2024

Humanistic psychology is an approach that looks at a person as a whole. It is a theory that has been developing over time and was founded by a collection of psychologists in the field. Among the most influential psychologists include doctors Carl Rogers and Abraham Maslow.
Professionals who practice by using a humanistic approach look at a person from the following perspective:
Sponsored by

Choose a therapist to work with and start healing with 20% off from BetterHelp.
Click Here“The whole is greater than the sum of its parts”
-Aristotle.
The humanistic approach does not focus on illness, challenge, or dysfunction. It does not pinpoint a specific area of need as a focus of attention. It looks at a person’s entire personality. Humanistic psychology places emphasis on the journey toward self-actualization. The term ‘self-actualization’ refers to a sense of personal fulfillment. It is achieved when a person feels they have reached their potential.
Self-Actualization
In humanistic psychology, a goal for an individual is to reach self-actualization. Self-actualization is a person’s ability to fulfill their potential. They become who they envision themselves to be. A person’s potential reflects on their personal goals and who they want to become. Self-actualization can be challenging to achieve. This is because it requires a person to close the gap between who they are and who they want to be.
A person’s self-concept is often not in line with their ideal self. Self-concept is how a person sees themselves. The ideal self is who a person wants to be. The bigger the gap between a person’s self-concept and the ideal self, the harder they will need to work to close it. Closing the gap helps a person reach self-actualization.
The gap between self-concept and the ideal self can cause personal strain. Specifically, it can negatively impact a client’s sense of self-esteem. People can often feel insecure and unhappy with themselves if they are not satisfied with their self-concept.
Humanistic therapy can be helpful for people who struggle with their self-esteem. Working toward the goal of reaching self-actualization can help build self-esteem and self-satisfaction. It helps promote inner peace. It also allows clients to confront the parts of themselves that make them unhappy or frustrated.
Reaching self-actualization is a challenging process. Not everyone can reach full self-actualization. The smaller the gap between self-concept and the ideal self, the more satisfied a client can feel with who they are. Self-actualization can be a powerful experience for a person. It can help with alleviating conditions of depression and anxiety. It can help people who are fearful and insecure, and people who are harboring resentments from their past.
Key Contributors To Humanistic Psychology
Carl Rogers had strong beliefs on what a ‘good life’ means. Most people tend to think of a good life as a goal. Contrary to popular belief, Rogers believed a good life to be a process. According to Rogers, a good life comes from being able to be your authentic self. To enjoy the journey of life, rather than making it be the end goal. This idea of The Good Life plays a critical role in client-centered therapy. It is also a key factor in his humanistic theory.
Carl Rogers
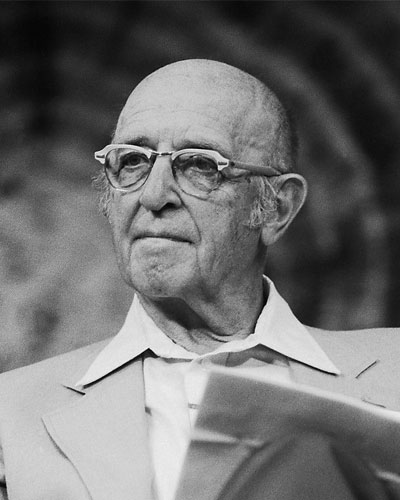

Carl Rogers was an American clinical psychologist. He believed that therapy can be helpful when a non-directive approach is used. A non-directive approach means the therapist does not direct the conversation. Instead, the client leads the conversation. They are given space to freely express their thoughts. This helps with the exploration and understanding of feelings.
Person-centered therapy was developed by Carl Rogers. In person-centered therapy, the client can lead the course of the therapy session. The role of the therapist is to take a passenger role along the journey with the client. This approach allows clients to feel a sense of power and control over the therapy session. It helps them take ownership of their personal growth in therapy.
Rogers believed that to achieve self-actualization, one must close the gap between:
Self-Concept
The self-concept refers to how a person sees themselves as who they are. It is a person’s impression of who they are in relation to the world around them. Self-concept is a powerful influence on a person and can affect each day of their life. It is developed from life experiences. Self-concept serves as a lens for how people see themselves and the world around them.
Self-concept is a powerful force in a person’s life that can be difficult to change. It affects a person’s self-esteem and beliefs about their motivations and potential. A person’s self-image is dependent on their self-concept. If they have a poor self-concept, they may reject their strengths or positive qualities. This makes self-concept an important factor that is addressed in humanistic therapy.
Ideal Self
The ideal self is who a person wants to be. The ideal self possesses attractive qualities the client desires but does not have. The gap between a person’s self-image and the ideal self can cause lower self-esteem. With person-centered therapy, the therapist uses different techniques to close this gap. This helps the client reach self-actualization. The following skills are used in person-centered therapy:
Empathy. According to Rogers, a therapist must use empathy in person-centered therapy sessions. Empathy refers to the ability to relate to a person’s life experiences. A person who can empathize can understand how a person feels in response to life challenges. Empathy also promotes understanding of a person’s thoughts and reasoning. The understanding is there even if the thoughts are not logical or if there is a disagreement.
Empathy helps a therapist understand how the client got to where they are. It also helps the client feel validated and understood without judgment. To succeed, the therapist must resist the urge to pass judgment or draw conclusions. Their role is to not agree or disagree, only to understand the client’s perspective.
Reflective Listening. Reflective listening is a method of expressing empathy for a client’s perspective. With reflective listening, the therapist takes on the goal of expressing understanding. They aim to communicate that they understand the client’s position. This means the therapist expresses understanding by reflecting on what the client shared.
Since the client is the leader of the journey, the therapist will not provide insight. They will also not ask a follow-up question. The therapist will remain in the role of passenger. This allows the client to continue to express themselves freely.
Congruence. Authenticity is important in person-centered therapy. For a client to progress in therapy, the journey with the therapist must feel authentic. This ensures a healthy and trusting relationship. Such a relationship promotes trust and openness to growth.
A therapist uses congruence to open their perspective. This helps them relate to the client’s feelings and experiences. The therapist aims to feel connected to the client. This helps the client feel understood and validated.
Congruence can help prevent the urge to problem-solve. Problem-solving can be counter-productive when aiming to reach self-actualization. In humanistic therapy, the focus is on the journey of the self. It is not about finding a solution to the problem or challenges in the client’s life.
Unconditional Positive Regard. Unconditional positive regard is a key component of self-actualization. Unconditional positive regard is the skill of the therapist to be unconditionally accepting. They embrace the client’s thoughts and feelings. They do not apply rules or conditions for the client’s experiences.
Unconditional positive regard helps the client be in tune with their journey. It helps them reach self-actualization. It provides space for them to confront their thoughts and feelings. They can do so without fear of judgment or pressure to conform to social expectations.
Abraham Maslow
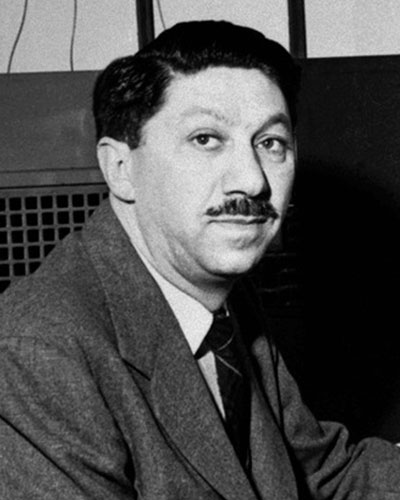

Abraham Maslow was an American psychologist. He contributed a great deal to the humanistic approach. Maslow found the focus of his research on what drives motivation. Through his research, he developed the hierarchy of needs. The hierarchy of needs is a 5-tier model of motivation. At the bottom of the hierarchy are basic needs. At the top of the hierarchy is self-actualization. Maslow believed that to reach self-actualization, a person must satisfy the needs of each tier.
The following are the 5 tiers in Maslow’s hierarchy of needs:
- Physiological Needs. Needs required for basic physiological survival. This includes food, water, air, and shelter.
- Safety Needs. Needs that ensure safety and security for life and status. This includes safety, shelter, financial stability, and access to resources for a healthy lifestyle.
- Love and Belongingness Needs. Needs to promote a sense of social belonging and connectedness with others. This includes friendship, family connections, and intimate partners.
- Esteem Needs. Needs that promote a sense of self. This includes good self-esteem, personal strength, self-respect, and respect for others.
- Self-Actualization Needs. Needs that are required to achieve self-actualization.
The hierarchy of needs theory states that not everyone will be able to meet all five needs of the hierarchy. Because of this, not everyone will be able to achieve self-actualization.
The following will be needed for the success of achieving all 5 tiers of the hierarchy of needs:
- Life changes
- Inner strength
- Resilience
Motivation to continue to move forward will depend on the individual.
Maslow believed that to reach self-actualization, you must satisfy the needs of each tier. He also recognized that life is imperfect. At times the needs of the tiers may not fall into sequential order. This means that there can be times when people either revert into previous tiers or skip tiers to maintain the needs of others.
Sponsored by

Find an affordable therapist online with 20% off from BetterHelp.
Click Here






Leave A Reply